Sri Lankan authorities issued shoot-on-sight orders on Tuesday to quell unrest that has seen buildings and vehicles set ablaze a day after the island was rocked by deadly violence and rioting.
With thousands of security forces enforcing a curfew, the defence ministry said troops “have been ordered to shoot on sight anyone looting public property or causing harm to life”.
On Monday, government supporters with sticks and clubs attacked demonstrators in Colombo protesting peacefully for weeks over a dire economic crisis and demanding President Gotabaya Rajapaksa’s resignation.
Mobs then retaliated across the country late into the night, torchingSr dozens of homes of ruling-party politicians and trying to storm the prime minister’s official residence in the capital.
Police said Tuesday eight people had died.
Protests continued on Tuesday despite the curfew, with some people defying the shoot-on-sight order to torch buildings and vehicles.
A luxury hotel said to belong to a Rajapaksa relative was set on fire on Tuesday evening on the edge of the Sinharaja rainforest.
And police shot into the air at two locations to disperse mobs trying to burn vehicles.
Earlier, a crowd had attacked and set fire to a vehicle carrying Colombo’s most senior policeman.
Officers fired warning shots and sent in reinforcements to rescue Senior Deputy Inspector-General Deshabandu Tennakoon, who was rushed to hospital but later released.
In another sign of deteriorating security, vigilante groups blocked the main road to Colombo airport to check for any Rajapaksa loyalists trying to leave the island, witnesses said.
As well as those killed, more than 225 people were injured on Monday, which also saw the resignation of prime minister Mahinda Rajapaksa.
His departure, however, failed to quell public anger, with his brother still president and wielding widespread powers including command over security forces.
Mahinda had to be rescued in a pre-dawn military operation after thousands of angry protesters stormed his official residence overnight and lobbed petrol bombs.
Protester Chamal Polwattage said he expected demonstrations to swell again and vowed they would not leave “until the president goes”.
The Rajapaksa clan’s hold on power has been shaken by months of blackouts and shortages of essential goods in Sri Lanka’s worst economic crisis since independence in 1948.
The pandemic torpedoed vital tourism and forced the government to halt most imports to save foreign currency needed to pay its debts, on which it has now defaulted.
But after weeks of peaceful demonstrations, Monday’s attacks on protesters by government supporters represented a turning point.
In the ensuing violence, police fired tear gas and water cannon to disperse crowds and declared a curfew across the entire South Asian nation until Wednesday, but later extended it by another day to Thursday.
Angry crowds set alight the homes of at least 42 pro-Rajapaksa politicians.
Several Rajapaksa homes were torched, while a family museum in their ancestral village was trashed.
UN rights chief Michelle Bachelet said Tuesday she was “deeply troubled” by the violence committed both by supporters of the government and the subsequent “mob violence” against ruling party members.
Bachelet in a statement called for an investigation and urged the government to “engage in meaningful dialogue with all parts of society”.
The US State Department also reiterated a call for an investigation into the clashes, saying Washington was both concerned with the escalating violence and the deployment of the military.
“We stress that peaceful protesters should never be subjected to violence or intimidation, whether that’s on the part of the military force or civilian units,” spokesman Ned Price told reporters.
Washington also urged Sri Lanka’s political authorities to quickly “ensure public safety” and identify “solutions to achieve long term economic and political stability.”
Wth inputs from NDTV
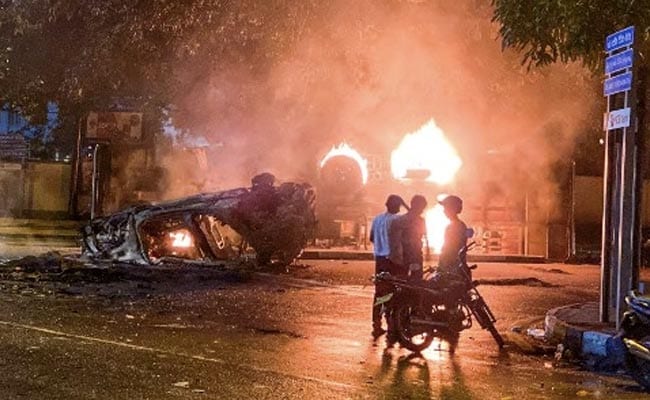



 Supreme Court holds all sedition law cases till review
Supreme Court holds all sedition law cases till review 