India’s economic growth figures seem to be getting increasingly delinked with domestic manufacturing, industrial output, and job generation. The manufacturing sector had a very little contribution to the country’s 6.5 percent GDP growth during the last financial year, the slowest in four years. Despite a good monsoon last year, the country’s agriculture sector growth rate in the second quarter (October-March) was 3.5 percent. The industrial growth rate for 2024-25 is estimated to be only four percent, also marking the lowest in the last four years. In April, the country’s industrial output slowed to an eight-month low at 2.7 percent as per the data released by the National Statistical Office (NSO). What is pushing the country’s GDP growth? Obviously, the less reliable estimates of the country’s vast services sector backed substantially by imports.
Ironically, India’s total imports in the last fiscal had grown by 6.85 percent, a little above the country’s GDP growth rate. This may give a somewhat wrong impression that the GDP growth is linked with the import growth. Uncontrolled imports, mainly from China, are dampening India’s domestic production initiative and new job generation agenda. China’s imports from India are rapidly shrinking. In the last fiscal, India’s imports from China grossed over $113 billion, a $11.5 percent rise over the previous fiscal. The top imported products from China included electrical and electronic equipment, machinery, organic chemicals, and plastics, most of which should have been manufactured in India. This increase contributed to a widening trade deficit for India. In contrast, India’s merchandise exports to China collapsed to only $14.25 billion from $16.66 billion, last year. Export-led China does not seem to like to import anything from India.
No one in the government appears to be concerned about the country’s massive import growth year after year, especially from China. Imports are mostly at the cost of domestic production and local jobs. A country does not import merchandise alone. It also imports labour that goes into the manufacturing of imported products. China continued to be India’s top import source, by far the biggest from any single country. In the last fiscal, India’s total imports are estimated to have grown to US$ 915.19 billion. This growth was driven by higher merchandise imports, which reached US$ 720.24 billion, a significant increase compared to the US$ 678.21 billion in the previous fiscal. No department in the government is willing to take the responsibility of the low and slow domestic industrial production and sinking job growth rates since the present BJP-led national government has been in operation. The government has been acting more like a dream merchant often seen busy in forecasting and focussing on India’s long-term economic prospects.
The so-called ‘Make-in-India’ initiative made little success in the absence of the import-happy government’s liberal investment policy, especially in manufacturing, that could strongly induce foreign industrial investors rush to India as they did in Communist China for several years. Foreign investors are not interested in the political colour of a government. In the first three months of 2025, the foreign direct investment (FDI) in China was as much as US$36.9 billion. Consider this against the FDI inflow of a mere $0.4 billion into India during the whole of 2024-25. It was $10.1 billion, a year ago. This is probably the worst performance in the country’s annual FDI inflow records while the government keeps talking about India emerging as a global manufacturing hub. India’s own industrial entrepreneurs are investing little in the country. Instead, they are indulging in investing abroad. During the last financial year, India’s net outward FDI (OFDI) grew 75 percent year on year to $29.2 billion. Singapore, the US, UAE, Mauritius and the Netherlands together accounted for more than half of the rise in OFDI.
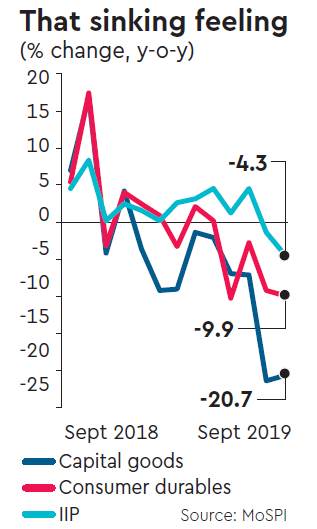
The country’s Index of Industrial Production (IIP) expanded by only four percent for the 2024-25 fiscal. This growth is lower than the 5.5 percent recorded in March 2024. The manufacturing sector experienced a further slowdown, with growth at 4.5 percent for the year, down from 12.3 percent in 2023-24. The IIP grew by only three percent in March 2025. The industrial output grew by four percent during the April-October period of the last financial year. The share of manufacturing in India’s GDP continues to be as low as 12 percent. According to Visual Capitalist, the share of manufacturing in China’s GDP is projected to be around 29 percent of global manufacturing output in 2025. This amplifies the significant dominance of China in global manufacturing, potentially matching or exceeding the combined share of the US and its allies. Specifically, China is projected to have a manufacturing output of $4.8 trillion, accounting for 29 percent of the global value.
Less than two months ago, India’s Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman said the country plans to raise the share of its manufacturing sector from 12 percent to 23 percent over the next two decades, aiming to create jobs and drive economic growth. While speaking at the Hoover Institution at California’s Stanford University, the finance minister said India is focussing on 14 identified sunrise sectors like semiconductors, renewable energy components, medical devices, batteries and labour-intensive industries, including leather and textile, to enhance the share of manufacturing in GDP.
However, of these industries, semiconductors may only appear to be a sunrise industry in India. Incidentally, the present form of the global semiconductor industry is almost 70-year-old. The first commercially available microprocessor, Intel 4004, was released in 1971. India is expected to launch its first locally produced semiconductor chip, under foreign equity and technical control, by the end of the current year. India is a major importer of semiconductors. Its local end-use market is projected to double from $54 billion in 2025 to $108 billion by 2030. Lately, the government’s highly liberal investment incentives are expected to bring foreign companies to help push up domestic semiconductors production.
Until recently, the government appeared to be rather casual about strengthening the country’s industrial and manufacturing bases. Even in 2014-15, when the Narendra Modi-led government came to power at the centre (May 26, 2014), India’s manufacturing sector contributed 16.3 percent to the country’s GDP. While the government’s much-touted ‘Make-in-India’ policy was launched in September 2014, hoping to fast-forward its share, the manufacturing sector’s contribution to GDP has subsequently declined mainly due to the lack of a strong commitment to the programme and uncontrolled import growth over the years. That may explain why the country’s annual GDP growth rate has generally failed to reflect on its growth of the manufacturing sector and employment. (IPA Service)
 Pak Politician Acknowledges Terror Legacy
Pak Politician Acknowledges Terror Legacy 